Step 2: Initialize Chat SDK
Feature Description
You must initialize the SDK before using its features. In most scenarios, you need to initialize the SDK only once during the application lifecycle.
Initialization
You can initialize the SDK in the following steps:
1. Prepare an
SDKAppID.2. Configure the
V2TIMSDKConfig object.3. Add an SDK event listener.
4. Call
initSDK to initialize the SDK.The detailed steps are as follows.
Preparing an SDKAppID
SDKAppID uniquely identifies an account. We recommend you apply for a new SDKAppID for each application. Messages are naturally isolated and cannot communicate between different SDKAppID values. To perform the initialization, you must have a correct SDKAppID.
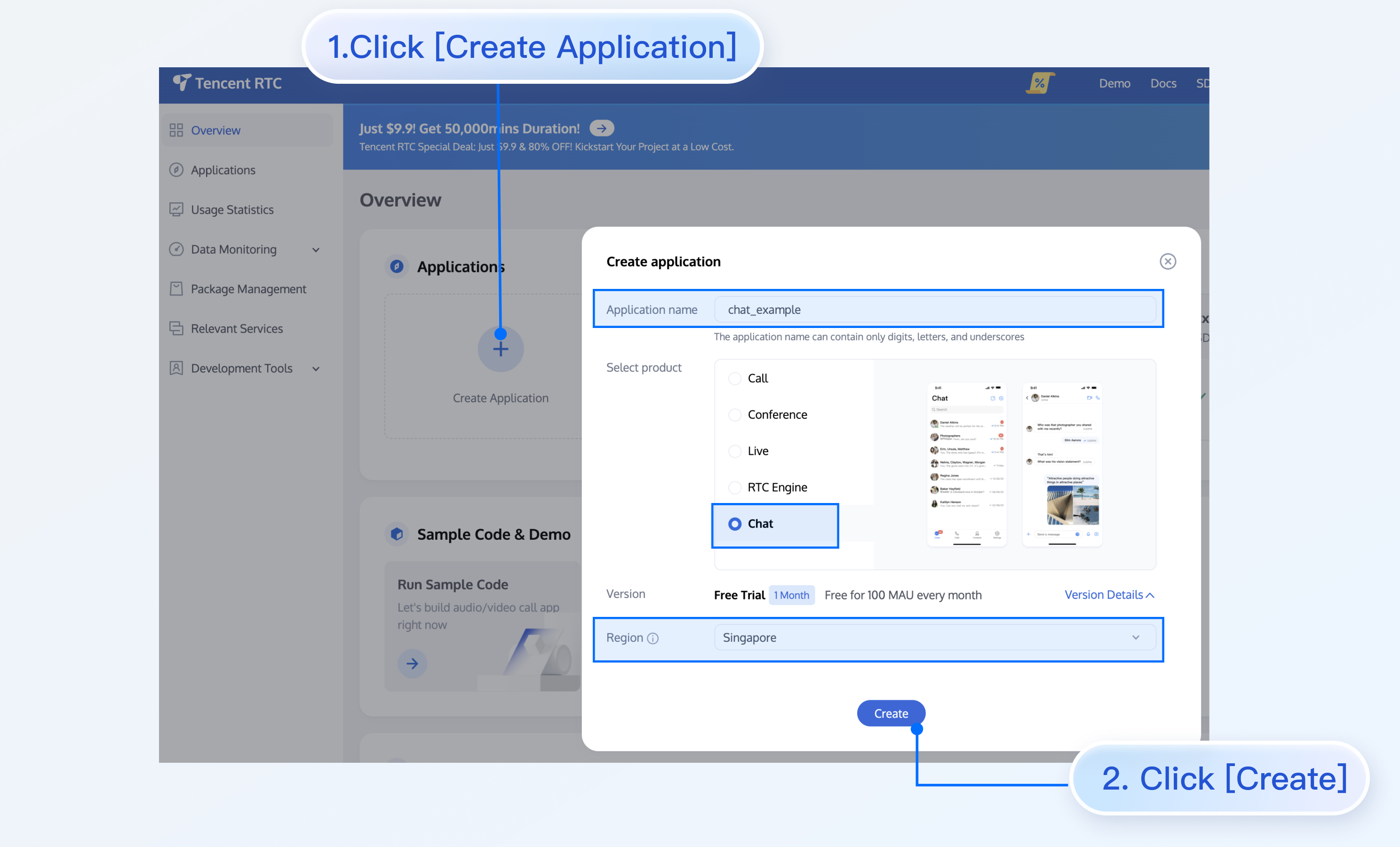
In the Chat Console, you can view all your SDKAppID values, and you can click Create Application to create an SDKAppID.
Configuring the V2TIMSDKConfig
Before initializing the SDK, you need to initialize the
V2TIMSDKConfig object (Java / Swift / Objective-C / C++), which is used to configure the SDK initially, such as setting the log level and log listening callback.Setting the log level
The SDK supports the following log levels:
Log Level | Log Output |
V2TIM_LOG_NONE | No log is output. |
V2TIM_LOG_DEBUG | Logs at the DEBUG, INFO, WARNING, and ERROR levels are output (default log levels). |
V2TIM_LOG_INFO | Logs at the INFO, WARNING, and ERROR levels are output. |
V2TIM_LOG_WARN | Logs at the WARNING and ERROR levels are output. |
V2TIM_LOG_ERROR | Logs at the ERROR level are output. |
SDK log storage rules are as follows:
Local SDK logs are retained for seven days by default, after which the logs will be automatically cleared during the SDK initialization.
By default, SDK logs on Android are stored in the
/sdcard/tencent/imsdklogs/application package name directory for versions earlier than v4.8.50 and in the /sdcard/Android/data/package name/files/log/tencent/imsdk directory for v4.8.50 or later.By default, SDK logs on iOS are stored in the
/Library/Caches/com_tencent_imsdk_log directory.By default, SDK logs on Windows are stored in the program's running directory. For example, when the program is running in the
C:\App directory, SDK will store logs in the C:\App\com_tencent_imsdk_log directory.
Starting from v4.7.1, the xlog module from WeChat is used to output SDK logs, which are compressed by default and must be decompressed by using the Python script.
To obtain the script for decompression, click Decode Log 27 (for Python 2.7) or Decode Log 30 (for Python 3.0).
In the Windows or macOS console, you can decompress log files by running the following command. After decompression, the file names end with "xlog.log", and you can use the text editor to open these files.
python decode_mars_nocrypt_log_file.py imsdk_yyyyMMdd.xlog
Setting a log listener
If you need to listen on SDK logs in real time, you can call
setLogListener (Java / Swift / Objective-C / C++) to set a log listener.
After it is set, the SDK will throw log information through this callback in real time.Note:
The callback is in the main thread. Log callbacks can be quite frequent, so be careful not to synchronize too many time-consuming tasks in the callback, which may block the main thread.
The sample code of configuring
V2TIMSDKConfig is as follows:// Initialize the `config` objectV2TIMSDKConfig config = new V2TIMSDKConfig();// Specify the log output levelconfig.setLogLevel(V2TIMSDKConfig.V2TIM_LOG_INFO);// Specify the log listenerconfig.setLogListener(new V2TIMLogListener() {@Overridepublic void onLog(int logLevel, String logContent) {// `logContent` is the SDK log content}});
// Initialize the `config` objectlet config = V2TIMSDKConfig()// Specify the log output levelconfig.logLevel = .V2TIM_LOG_INFO// Set the log listenerconfig.logListener = { logLevel, logContent in// `logContent` is the SDK log contentprint("Log Level: \(logLevel), Log Content: \(logContent)")}
// Initialize the `config` objectV2TIMSDKConfig *config = [[V2TIMSDKConfig alloc] init];// Specify the log output levelconfig.logLevel = V2TIM_LOG_INFO;// Set the log listenerconfig.logListener = ^(V2TIMLogLevel logLevel, NSString *logContent) {// `logContent` is the SDK log content};
class LogListener final : public V2TIMLogListener {public:LogListener() = default;~LogListener() override = default;void OnLog(V2TIMLogLevel logLevel, const V2TIMString& logContent) override {// `logContent` is the SDK log content}};// Note that `logListener` should not be released before the SDK is uninitialized,// otherwise the log callback cannot be called.LogListener logListener;// Initialize the `config` objectV2TIMSDKConfig config;// Specify the log output levelconfig.logLevel = V2TIMLogLevel::V2TIM_LOG_INFO;// Specify the log listenerconfig.logListener = &logListener;
Adding an SDK event listener
After the initialization, the SDK will report such events as connection status and login ticket expiration through
V2TIMSDKListener.
We recommend you call the addIMSDKListener API (Java / Swift / Objective-C / C++) to add an SDK event listener and perform logic processing in the corresponding callback.V2TIMSDKListener callbacks are as follows:Event Callback | Description | Recommended Operation |
onConnecting | The SDK is connecting to the CVM instance. | Display the "connecting" status on the UI. |
onConnectSuccess | The SDK is successfully connected to the CVM instance. | - |
onConnectFailed | The SDK failed to connect to the CVM instance. | Notify the user that the network connection is currently unavailable. |
onKickedOffline | The current user is kicked offline. | Display the "You are already logged in on another device. Are you sure you want to log in again?" message on the UI. |
onUserSigExpired | The login ticket expired. | Log in with a new UserSig. |
onSelfInfoUpdated | The current user's profile is updated. | Update the profile photo and nickname on the UI. |
Note:
If you receive the
onUserSigExpired callback, the UserSig that you use for login has expired. In this case, you need to use a new UserSig to log in again. If you continue to use the expired UserSig, the SDK will be in an infinite login loop.Sample code:
// The `sdkListener` type is `V2TIMSDKListener`.V2TIMManager.getInstance().addIMSDKListener(sdkListener);
// The `self` type is id<V2TIMSDKListener>.V2TIMManager.shared.addIMSDKListener(listener: self)
// The `self` type is id<V2TIMSDKListener>.[[V2TIMManager sharedInstance] addIMSDKListener:self];
// `sdkListener` is an instance of V2TIMSDKListener.V2TIMManager::GetInstance()->AddSDKListener(&sdkListener);
Calling the initialization API
After performing the above steps, you can call
initSDK (Java / Swift / Objective-C / C++) to initialize the SDK.Sample code:
// 1. Get the `SDKAppID` from the IM console.// 2. Initialize the `config` object.V2TIMSDKConfig config = new V2TIMSDKConfig();// 3. Specify the log output level.config.setLogLevel(V2TIMSDKConfig.V2TIM_LOG_INFO);// 4. Add the `V2TIMSDKListener` event listener. `sdkListener` is the implementation class of `V2TIMSDKListener`. If you don't need to listen to SDK events, skip this step.V2TIMManager.getInstance().addIMSDKListener(sdkListener);// 5. Initialize the SDK. You can call the login API as soon as you call this API.int sdkAppID = 1400000000; // please set the sdkAppID of your own applicationV2TIMManager.getInstance().initSDK(context, sdkAppID, config);
// 1. Get the `SDKAppID` from the IM console.// 2. Initialize the `config` object.let config = V2TIMSDKConfig()// 3. Specify the log output level.config.logLevel = .V2TIM_LOG_INFO // Use enumeration values// 4. Add the `V2TIMSDKListener` event listener. `self` is the implementation class of id<V2TIMSDKListener>. If you don't need to listen to SDK events, skip this step.V2TIMManager.shared.addIMSDKListener(listener: self)// 5. Initialize the SDK. You can call the login API as soon as you call this API.V2TIMManager.shared.initSDK(sdkAppID: sdkAppID, config: config)
// 1. Get the `SDKAppID` from the IM console.// 2. Initialize the `config` object.V2TIMSDKConfig *config = [[V2TIMSDKConfig alloc] init];// 3. Specify the log output level.config.logLevel = V2TIM_LOG_INFO;// 4. Add the `V2TIMSDKListener` event listener. `self` is the implementation class of id<V2TIMSDKListener>. If you don't need to listen to SDK events, skip this step.[[V2TIMManager sharedInstance] addIMSDKListener:self];// 5. Initialize the SDK. You can call the login API as soon as you call this API.int sdkAppID = 1400000000; // please set the sdkAppID of your own application[[V2TIMManager sharedInstance] initSDK:sdkAppID config:config];
// 1. Get the `SDKAppID` from the IM console.// 2. Initialize the `config` object.V2TIMSDKConfig config;// 3. Specify the log output level.config.logLevel = V2TIMLogLevel::V2TIM_LOG_INFO;// 4. Add the `V2TIMSDKListener` event listener. `sdkListener` is the implementation class of `V2TIMSDKListener`.// If you don't need to listen to SDK events, skip this step.V2TIMManager::GetInstance()->AddSDKListener(&sdkListener);// 5. Initialize the SDK. You can call the login API as soon as you call this API.int sdkAppID = 1400000000; // please set the sdkAppID of your own applicationV2TIMManager::GetInstance()->InitSDK(sdkAppID, config);
Uninitialization
Generally, if your application's lifecycle is the same as the SDK's lifecycle, you don't need to uninitialize the SDK before exiting the application.
However, you can uninitialize the SDK in special cases, for example, only after you enter a specific UI and no longer use it after exiting the UI.
Uninitialization requires two steps:
1. If you have called
addIMSDKListener to add the SDK listener, call removeIMSDKListener (Java / Swift / Objective-C / C++) to remove it.2. Call the
unInitSDK uninitialization API (Java / Swift / Objective-C / C++).Sample code:
// Remove the `V2TIMSDKListener` event listener. `sdkListener` is the implementation class of `V2TIMSDKListener`.V2TIMManager.getInstance().removeIMSDKListener(sdkListener);// Uninitialize the SDKV2TIMManager.getInstance().unInitSDK();
// `self` is the implementation class of id<V2TIMSDKListener>.V2TIMManager.shared.removeIMSDKListener(listener: self)// Uninitialize the SDKV2TIMManager.shared.unInitSDK()
// `self` is the implementation class of id<V2TIMSDKListener>.[[V2TIMManager sharedInstance] removeIMSDKListener:self];// Uninitialize the SDK[[V2TIMManager sharedInstance] unInitSDK];
// Remove the `V2TIMSDKListener` event listener. `sdkListener` is the instance of V2TIMSDKListener.V2TIMManager::GetInstance()->RemoveSDKListener(&sdkListener);// Uninitialize the SDKV2TIMManager::GetInstance()->UnInitSDK();
FAQs
1. What should I do if error code 6013 is returned along with the description "not initialized" when I call the login or another API?
You must initialize the SDK before using the login, message, group, conversation, relationship chain and profile, and signaling features.