Login State
Introduction
LoginState is a state management center related to login, specialized in managing login states and operations. It provides automatic login, manual login, logout, and other features, and supports real-time monitoring of login status and error handling.The Hook has the following features:
Auto login management - Supports automatic initialization and login after configuration
Manual login control - Provides manual login and logout methods
Real-time status synchronization - Updates login status and error information in real time
Duplicate login prevention - Prevents duplicate login and intelligent processing during configuration change
UseLoginState Parameter
Value | Type | Description |
config | LoginConfig | login configuration |
config is a login parameter for initializing login status. Direct use in the component enables automatic login.LoginConfig definition as follows:interface LoginConfig {userID: string; // user IDSDKAppID: number; // application IDuserSig: string; // user signatureonSuccess?: () => void; // login success callbackonError?: (error: Error) => void; // login failure callback}
UseLoginState Return Value
Value | Type | Description |
status | LoginStatus | Current log-in status |
error | Error | null | Error info during log-in |
currentConfig | LoginConfig | null | currently used login configuration |
login | (config: LoginConfig) => Promise<void> | Manual login method |
logout | () => Promise<void> | Logout method |
Field Description
status
Type:
LoginStatusDescription: Current log-in status, used to track each stage of the login process.
Enum definition:
enum LoginStatus {IDLE, // Idle, not startedLOADING, // Logging inSUCCESS, // Login succeededERROR, // Login failed}
error
Type:
Error | nullDescription: Error occurred during log-in. It is
null when login succeeded or no error occurred.currentConfig
Type:
LoginConfig | nullDescription: Currently used login configuration. Used to compare configuration changes and prevent duplicate logins.
login
Type:
(config: LoginConfig) => Promise<void>Description: Manual login method. Complete login configuration can be passed in to log in.
Parameter:
config - Login configuration objectReturn value:
Promise<void> - Login complete Promiselogout
Type:
() => Promise<void>Description: Logout method. Clears login status and calls the SDK's logout API.
Return value:
Promise<void> - Logout complete PromiseUsage Examples
Method One: Auto Login (Recommended)
The simplest way to use: input login configuration to automatically initialize and log in.
import React from 'react';import { useLoginState, LoginStatus } from './states/LoginState/LoginState';function App() {const { status, error, logout } = useLoginState({userID: 'your-userID-here',SDKAppID: 0, // your-SDKAppID-here, this is number type!userSig: 'your-userSig-here',onSuccess: () => console.log('🎉 Login successful.'),onError: (error) => console.error('❌ Login failed:', error),});// Render different content based on log-in statusif (status === LoginStatus.LOADING) {return <div className="loading">Logging in...</div>;}if (status === LoginStatus.ERROR) {return (<div className="error"><p>Login failed: {error?.message}</p><button onClick={() => window.location.reload()}>Retry</button></div>);}if (status !== LoginStatus.SUCCESS) {return <div className="waiting">Waiting to log in...</div>;}return (<div className="app"><header className="app-header"><h1>chat app</h1><button onClick={logout} className="logout-btn">Log out</button></header><UIKitProvider></UIKitProvider></div>);}export default App;
Method 2: Manual Control Logon
This approach offers more control and allows manual triggering of logon when needed.
import React, { useState } from 'react';import { useLoginState, LoginStatus } from './states/LoginState/LoginState';function ManualLoginApp() {const { login, logout, status, error, client } = useLoginState(); // No config passedconst [loginForm, setLoginForm] = useState({userID: '',SDKAppID: 0,userSig: '',});const handleLogin = async () => {try {await login({...loginForm,onSuccess: () => {console.log('Login successful.');// Here you can log in and perform operations},onError: (error) => {console.error('Login failed:', error);// Here you can fix login errors},});} catch (error) {console.error('Log-in exception:', error);}};const handleLogout = async () => {try {await logout();console.log('Logout successful.');} catch (error) {console.error('Logout failed:', error);}};const isLoggedIn = status === LoginStatus.SUCCESS;return (<div className="manual-login-app">{!isLoggedIn ? (<div className="login-form"><h2>Login</h2><div className="form-group"><label>User ID:</label><inputtype="text"value={loginForm.userID}onChange={(e) => setLoginForm(prev => ({ ...prev, userID: e.target.value }))}placeholder="Enter user ID"/></div><div className="form-group"><label>SDK App ID:</label><inputtype="number"value={loginForm.SDKAppID}onChange={(e) => setLoginForm(prev => ({ ...prev, SDKAppID: Number(e.target.value) }))}placeholder="Enter SDK App ID"/></div><div className="form-group"><label>User Signature:</label><textareavalue={loginForm.userSig}onChange={(e) => setLoginForm(prev => ({ ...prev, userSig: e.target.value }))}placeholder="Enter user signature"/></div><buttononClick={handleLogin}disabled={status === LoginStatus.LOADING}className="login-btn">{status === LoginStatus.LOADING ? 'Logging in...' : 'Login'}</button>{error && (<div className="error-message">Error: {error.message}</div>)}</div>) : (<div className="app-content"><div className="app-header"><h1>chat app</h1><button onClick={handleLogout} className="logout-btn">Log out.</button></div><ChatApp client={client} /></div>)}</div>);}export default ManualLoginApp;
The rendering is shown below:
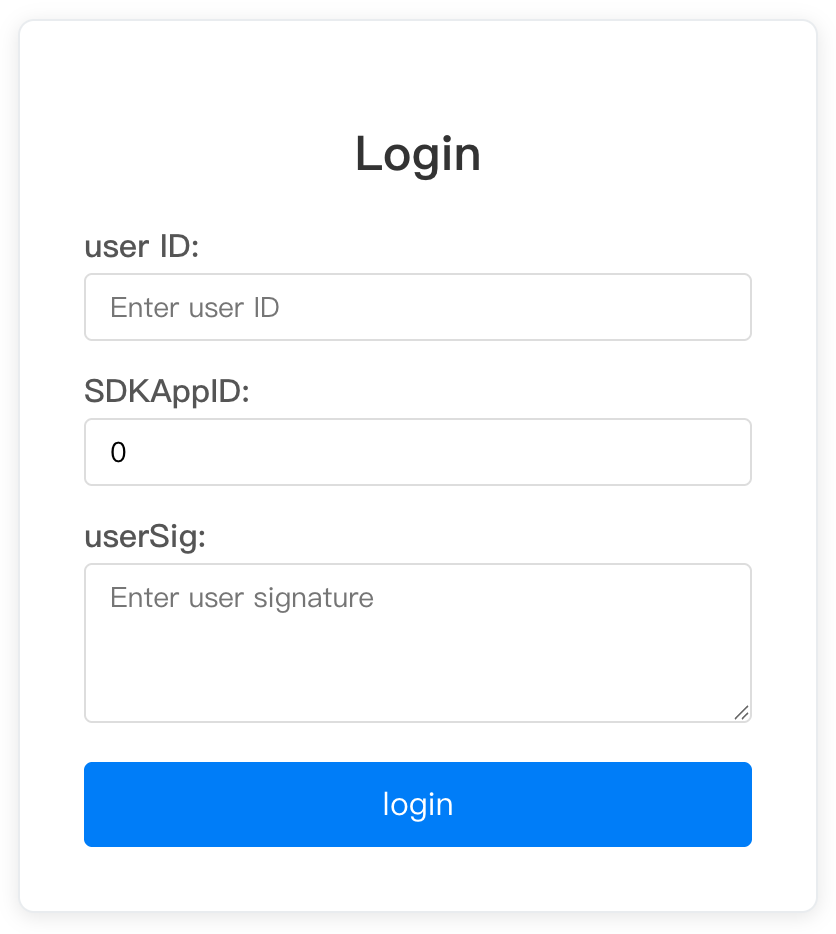
Style Reference
The following is the supporting SCSS style, which can be adjusted as needed:
// basic style.loading {display: flex;justify-content: center;align-items: center;height: 100vh;font-size: 18px;color: #666;}.error {display: flex;flex-direction: column;justify-content: center;align-items: center;height: 100vh;p {color: #ff4444;margin-bottom: 16px;}button {padding: 8px 16px;background: #007bff;color: white;border: none;border-radius: 4px;cursor: pointer;&:hover {background: #0056b3;}}}// Apply style.app {height: 100vh;display: flex;flex-direction: column;.app-header {display: flex;justify-content: space-between;align-items: center;padding: 16px 24px;background: #f8f9fa;border-bottom: 1px solid #e9ecef;h1 {margin: 0;color: #333;}.logout-btn {padding: 8px 16px;background: #dc3545;color: white;border: none;border-radius: 4px;cursor: pointer;&:hover {background: #c82333;}}}}// Manual login form style.manual-login-app {height: 100vh;display: flex;justify-content: center;align-items: center;.login-form {width: 400px;padding: 32px;border: 1px solid #e9ecef;border-radius: 8px;background: white;box-shadow: 0 2px 10px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);h2 {text-align: center;margin-bottom: 24px;color: #333;}.form-group {margin-bottom: 16px;label {display: block;margin-bottom: 4px;color: #555;font-weight: 500;}input, textarea {width: 100%;padding: 8px 12px;border: 1px solid #ddd;border-radius: 4px;font-size: 14px;&:focus {outline: none;border-color: #007bff;}}textarea {height: 80px;resize: vertical;}}.login-btn {width: 100%;padding: 12px;background: #007bff;color: white;border: none;border-radius: 4px;font-size: 16px;cursor: pointer;&:hover:not(:disabled) {background: #0056b3;}&:disabled {background: #ccc;cursor: not-allowed;}}.error-message {margin-top: 12px;padding: 8px;background: #f8d7da;color: #721c24;border-radius: 4px;font-size: 14px;}}}
Precautions
1. Parameter validation: Underwrite the passed in
userID, SDKAppID and userSig are effective.2. Error handling: Always handle possible login errors
3. Listen for status: Reasonably use login status to control UI display
4. Resource cleanup: Call the
logout method promptly during component uninstallation.5. Security: Do not hard-code sensitive information on the client.
userSig should be retrieved from the server.