Android
This document describes how to quickly integrate the
TUICallKit component. Performing the following key steps generally takes about ten minutes, after which you can implement the video call feature with complete UIs.Environment Preparations
Android 5.0 (SDK API level 21) or later.
Gradle 4.2.1 or later.
Mobile phone on Android 5.0 or later.
Step 1. Activate the Service
Before using the audio and video services provided by Tencent Cloud, you need to go to the Console to activate the audio and video service for your application. For specific steps, please refer to Activating the Service.
Step 2. Download and Import the Component
Go to GitHub, clone or download the code, and copy the
tuicallkit-kt subdirectory in the Android directory to the directory at the same level as app in your current project, as shown below: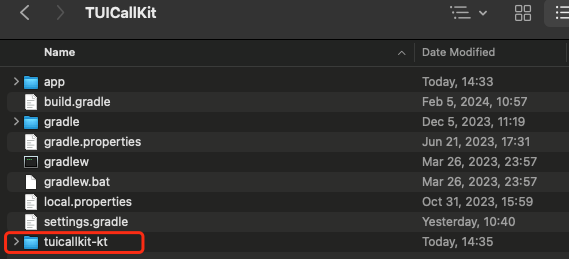
Step 3. Configure the Project
1. Find the
settings.gradle(or settings.gradle.kts) file in the project root directory and add the following code to import the TUICallKit component downloaded in step 2 to your current project:include ':tuicallkit-kt'
include(":tuicallkit-kt")
2. Find the
build.gradle(or build.gradle.kts) file in the app directory and add the following code to declare the dependencies of the current application on the component just added:api project(':tuicallkit-kt')
api(project(":tuicallkit-kt"))
Note
The
TUICallKit project depends on TRTC SDK, Chat SDK, tuicallengine, and the tuicore public library internally by default with no need of additional configuration. To upgrade the version, modify the tuicallkit-kt/build.gradle file.3. As the SDK uses Java's reflection feature internally, you need to add certain classes in the SDK to the obfuscation allowlist by adding the following code to the
proguard-rules.pro file:-keep class com.tencent.** { *;}
Note
TUICallKit helps you apply for camera, mic, and storage read/write permissions internally. If you need more or fewer permissions based on your actual business conditions, you can modify tuicallkit-kt/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml.Step 4. Log in to the TUICallKit Component
Add the following code to your project to call the relevant APIs in
TUICore to log in to the TUICallKit component. This step is very important, as the user can use the component features properly only after a successful login. Make sure the relevant parameters are correctly configured:TUILogin.login(context,1400000001, // Replace it with the `SDKAppID` obtained in step 1."denny", // Replace it with your `UserID`."xxxxxxxxxxx", // You can calculate a `UserSig` in the console and enter it here.object : TUICallback() {override fun onSuccess() {}override fun onError(errorCode: Int, errorMessage: String) {}})}
Parameter description: The key parameters used by the
login function are as detailed below:SDKAppID: Obtained in the last step in step 1 and no details are required here.
UserID: The ID of the current user, which is a string that can contain only letters (a–z and A–Z), digits (0–9), hyphens (-), or underscores (_).
UserSig: The authentication credential used by Tencent Cloud to verify whether the current user is allowed to use the TRTC service. You can get it by using the
SDKSecretKey to encrypt the information such as SDKAppID and UserID. You can generate a temporary UserSig by clicking the UserSig Generate button in the console.For more information, see UserSig.
Note
Many developers have contacted us with many questions regarding this step. Below are some of the frequently encountered problems:
SDKAppID is invalid.
UserSig is set to the value of Secretkey by mistake. The UserSig is generated by using the SecretKey for the purpose of encrypting information such as SDKAppID, UserID, and the expiration time. But the value of the UserSig that is required cannot be directly substituted with the value of the SecretKey.
UserID is set to a simple string such as 1, 123, or 111, and your colleague may be using the same userId while working on a project simultaneously. In this case, login will fail as TRTC doesn't support login on multiple terminals with the same UserID. Therefore, we recommend you use some distinguishable userId values during debugging.
The sample code on GitHub uses the
genTestUserSig function to calculate UserSig locally, so as to help you complete the current access process faster. However, this scheme exposes your SecretKey in the application code, which makes it difficult for you to upgrade and protect your SecretKey subsequently. Therefore, we strongly recommend you run the UserSig calculation logic on the server and make the application request the UserSig calculated in real time from your server every time the application uses the TUICallKit component.Step 5. Make Your First Call
After the caller and callee have successfully signed in, the caller can initiate an audio or video call by calling the TUICallKit's call method and specifying the call type and callee's userId. The callee will then receive the incoming call invitation.
//Make a 1v1 video call (assuming UserID is mike)TUICallKit.createInstance(context).call("mike", TUICallDefine.MediaType.Video)
// Make a 1v1 video call (assuming UserID is mike)TUICallKit.createInstance(context).call("mike", TUICallDefine.MediaType.Video);
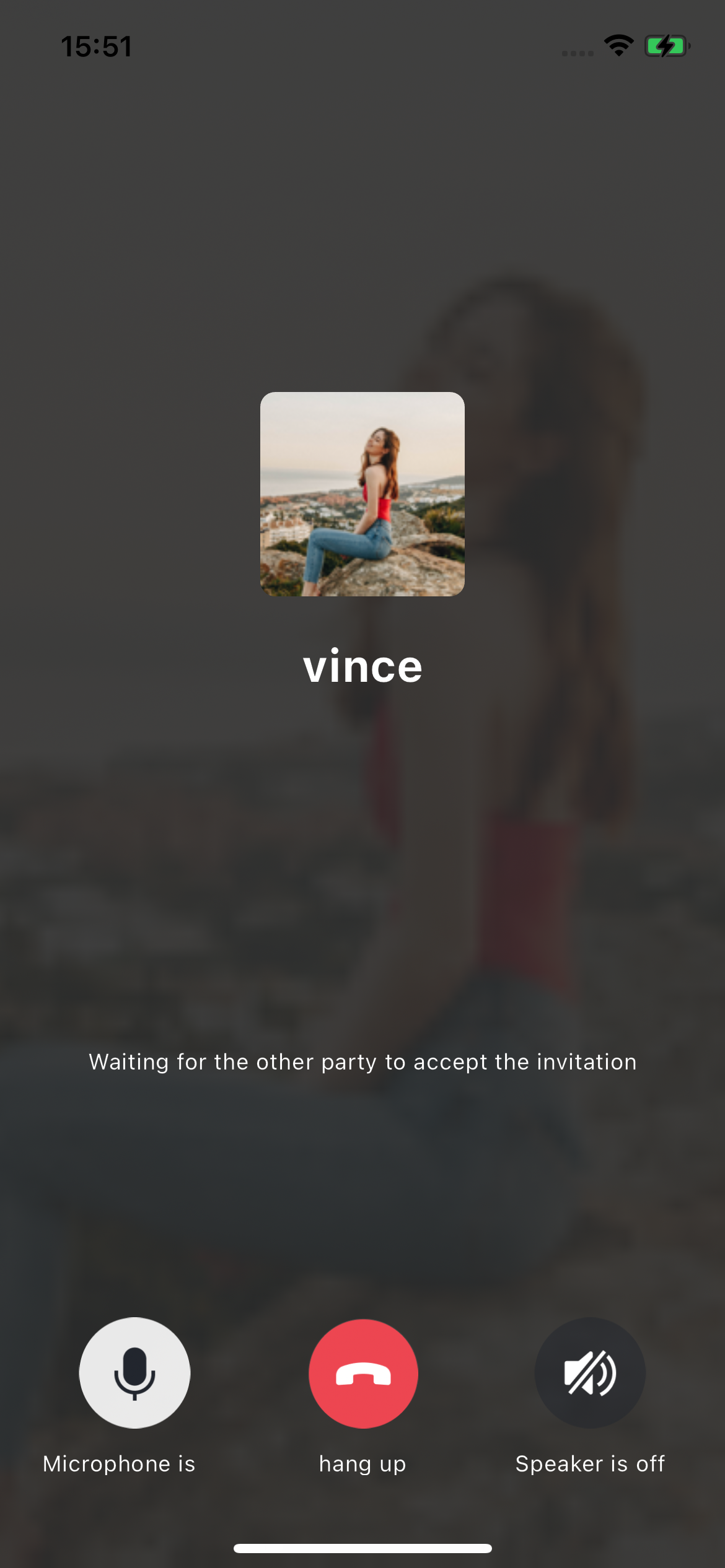 | 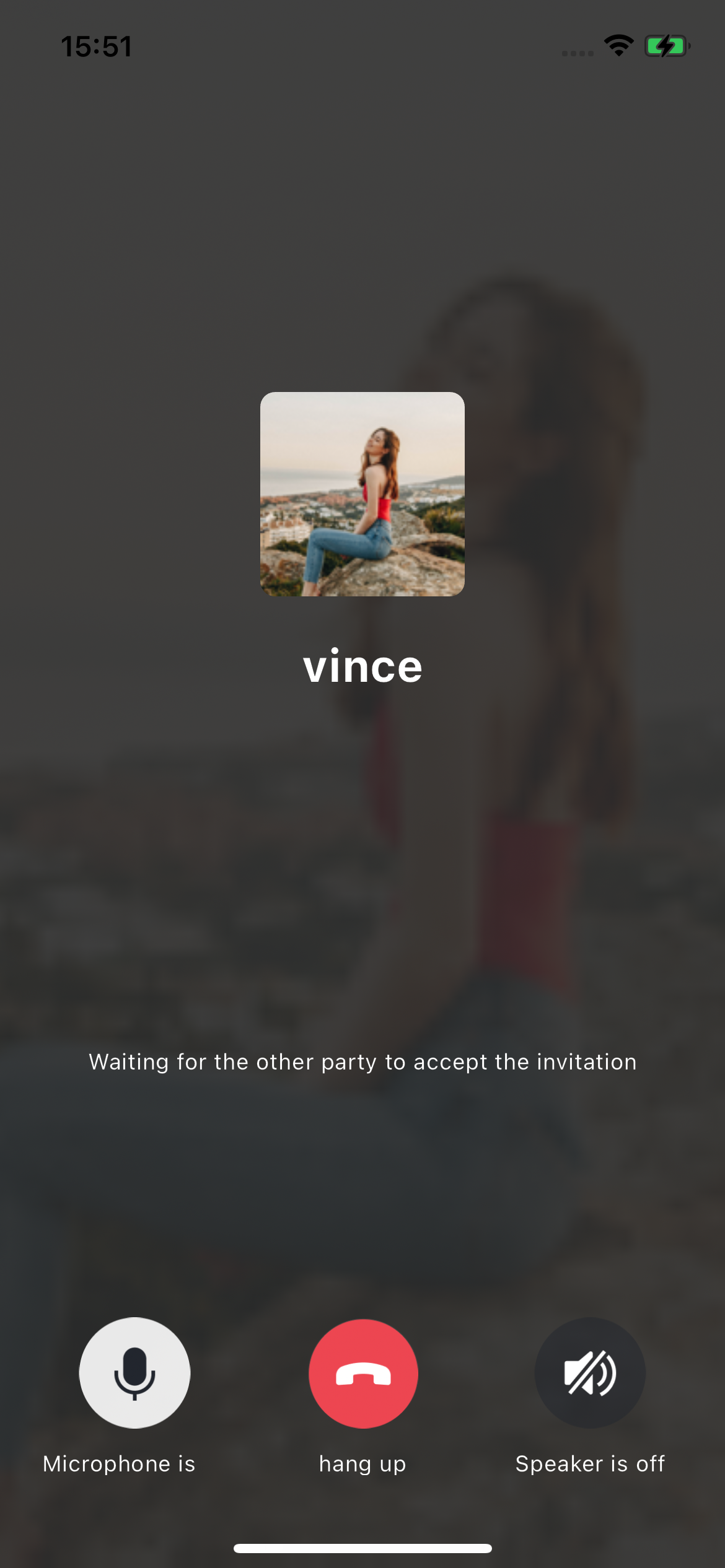 |
Caller | Callee |
Additional Features
FAQs
1. What should I do if I receive the error message "The package you purchased does not support this ability"?
The error message indicates that your application's audio/video call capability package has expired or is not activated. You can claim or activate the audio/video call capability as instructed in step 1 to continue using
TUICallKit.2. What should I do if TUICallKit crashes and outputs the log "No implementation found for xxxx"?
Below is the stack information:
java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError: No implementation found for void com.tencent.liteav.base.Log.nativeWriteLogToNative(int, java.lang.String, java.lang.String) (tried Java_com_tencent_liteav_base_Log_nativeWriteLogToNative and Java_com_tencent_liteav_base_Log_nativeWriteLogToNative__ILjava_lang_String_2Ljava_lang_String_2)at com.tencent.liteav.base.Log.nativeWriteLogToNative(Native Method)at com.tencent.liteav.base.Log.i(SourceFile:177)at com.tencent.liteav.basic.log.TXCLog.i(SourceFile:36)at com.tencent.liteav.trtccalling.model.impl.base.TRTCLogger.i(TRTCLogger.java:15)at com.tencent.liteav.trtccalling.model.impl.ServiceInitializer.init(ServiceInitializer.java:36)at com.tencent.liteav.trtccalling.model.impl.ServiceInitializer.onCreate(ServiceInitializer.java:101)at android.content.ContentProvider.attachInfo(ContentProvider.java:2097)at android.content.ContentProvider.attachInfo(ContentProvider.java:2070)at android.app.ActivityThread.installProvider(ActivityThread.java:8168)at android.app.ActivityThread.installContentProviders(ActivityThread.java:7709)at android.app.ActivityThread.handleBindApplication(ActivityThread.java:7573)at android.app.ActivityThread.access$2600(ActivityThread.java:260)at android.app.ActivityThread$H.handleMessage(ActivityThread.java:2435)at android.os.Handler.dispatchMessage(Handler.java:110)at android.os.Looper.loop(Looper.java:219)at android.app.ActivityThread.main(ActivityThread.java:8668)at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Native Method)at com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit$MethodAndArgsCaller.run(RuntimeInit.java:513)at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.main(ZygoteInit.java:1109)
If the above exception occurs on a real device, it is because some APIs of SDKs such as the TRTC SDK depended on by
TUICallKit are implemented through JNI, but Android Studio may not package native .so libraries when compiling the APK under some conditions. In this case, just clean the project again.Suggestions and Feedback
If you have any suggestions or feedback, please contact info_rtc@tencent.com.