Speech to Text and Translation
Use Cases
Tencent Real-Time Communication (TRTC) supports speech to text and translation. It can transcribe the audio streams of specified users or all users in a room into text, and translate them into other languages via AI, providing versatile solutions such as real-time captions and translation.
Prerequisites
Log in to the TRTC console, activate the TRTC service, and create an RTC-Engine application.
Purchasing RTC-Engine package (Lite version or above) unlocks the speech to text and real-time translation features.
Note:
The speech-to-text and real-time translation features are billed based on usage. For details, see Pricing.
Feature Overview
After a task is initiated, the TRTC AI Service launches an Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) bot to join the TRTC room and subscribe to the streams of specified users or all users for speech-to-text recognition. The recognition results are then delivered to both the client and server in real time via callbacks.
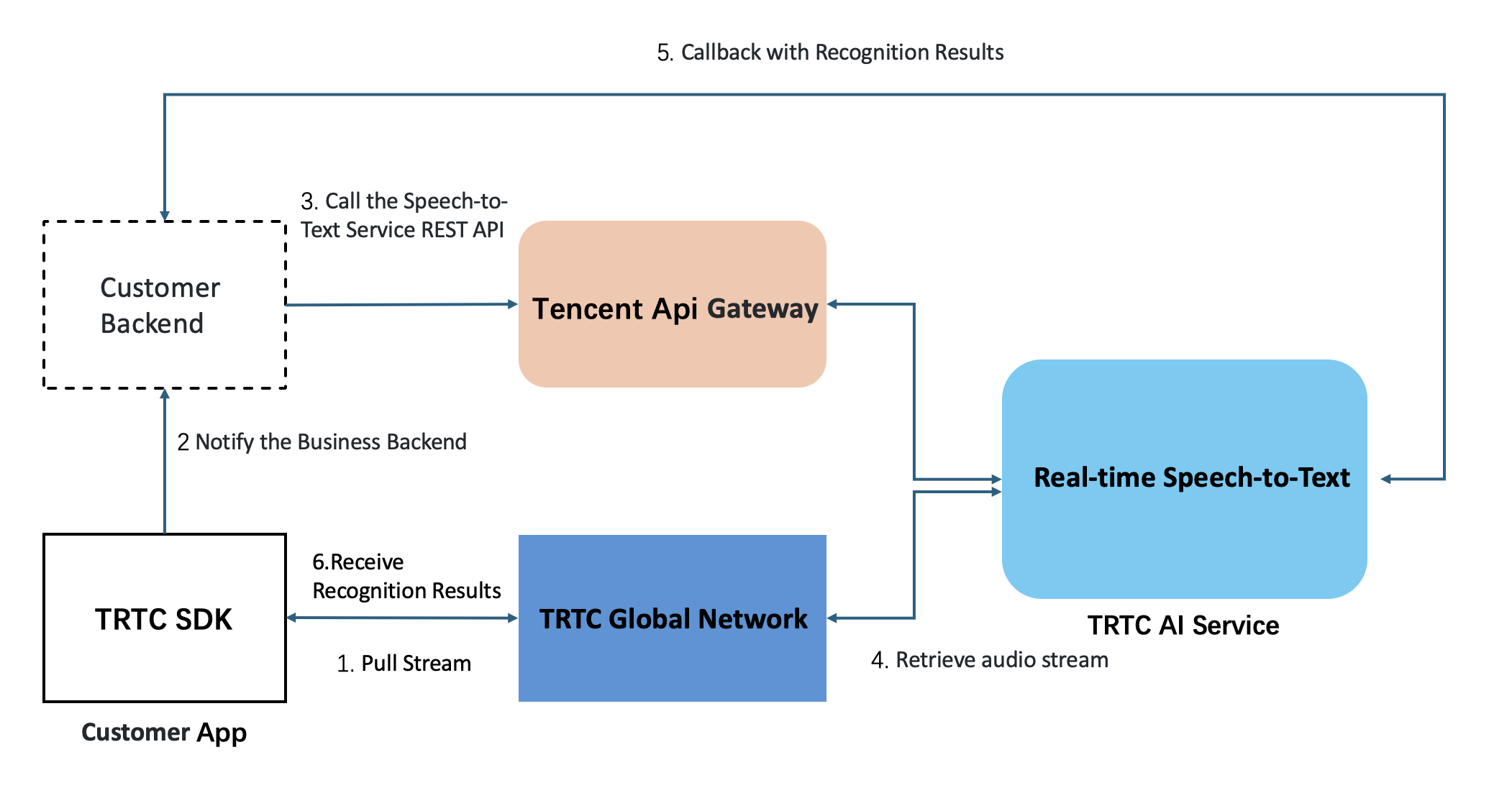
Integration Guide
Step 1: Receiving Speech-to-Text Results
Method 1: Receiving Text Messages via Client SDK
By using the custom message feature of the TRTC SDK, the client can listen for callback events to receive real-time speech-to-text and translation results. The format of the client callback message is as follows (Web client example):
trtc.on(TRTC.EVENT.CUSTOM_MESSAGE, event => { // Receive custom messages. // event.userId: The userId of the ASR robot. // event.cmdId: The message ID, which is fixed at 1 for transcriptions and captions. // event.seq: The sequence number of a message. // event.data: ArrayBuffer type. For content of transcriptions or captions, see the explanation of the data field below. const data = new TextDecoder().decode(event.data) // Explanation of the data field is as follows. console.log(`received custom msg from ${event.userId}, message: ${ data }`) })
Data field Description (Real-Time Captions)
Field Name | Type | Meaning |
type | Integer | 10000: When there are real-time captions and a complete sentence, the message type will be delivered. |
sender | String | Speaker's userid. |
receiver | Array | List of receiver userid. The message is actually broadcast within the room. |
payload.text | String | Recognized text, Unicode encoded. |
payload.start_time | String | Message start time. It is the absolute time after a task starts. |
payload.end_time | String | Message end time. It is the absolute time after a task starts. |
payload.end | Boolean | If true, this indicates a complete sentence |
{"type": 10000,"sender": "user_a","payload": {"text":"","start_time":"00:00:02","end_time":"00:00:05","end": true}}
Real-Time Translation Message
{"type": 10000,"sender": "ai_951073","payload": {"start_time_ms": 1760,"end_time_ms": 5530,"end": false,"roundid": "e6330a3c-eed7-40bb-8229-9bbe733a313f", // Unique ID for each conversation round"translation_text": "simultaneous interpretation of the meeting", // Translated text"translation_language": "en", // Language code of the translation"taskid": "x-dPLCz" // Unique identifier of the transcription task}}
Note:
Callback example:
Transcription: The complete sentence is transcribed and pushed once.
"How's the weather today?"
Captions & Translation: Caption or translation results are pushed incrementally in segments, with each subsequent segment including the previous content to deliver a real-time captioning effect.
"How"
"How's the weather"
"How's the weather today?"
Message Sequence: Caption message > Caption message > .... > Caption message (end = true)
Method 2: Receiving via Server-side Callbacks
The speech-to-text service also provides server-side event callbacks, facilitating your service to receive real-time conversation messages. See Detailed Callback Events.
Step 2: Initiating a Speech-to-Text and Translation Task
TRTC provides the following Tencent Cloud APIs for initiating and managing speech-to-text and translation tasks:
Start a speech-to-text task: StartAITranscription
Query a speech-to-text task: DescribeAITranscription
Stop a speech-to-text task: StopAITranscription
Start real-time translation task: Configure the TranslationConfig parameter in the input of StartAITranscription; Specify the target translation languages in TargetLanguages, e.g., ["en", "ja"]. Currently, the following target languages are supported:
Language Code | Language Name |
"zh" | Chinese |
"en" | English |
"es" | Spanish |
"pt" | Portuguese |
"fr" | French |
"de" | German |
"ru" | Russian |
"ar" | Arabic |
"ja" | Japanese |
"ko" | Korean |
"vi" | Vietnamese |
"ms" | Malay |
"id" | Indonesian |
"it" | Italian |
"th" | Thai |
Note:
The Speech-to-Text and Real-time Translation features support up to 100 concurrent tasks per SDKAppId. To increase this limit, please submit a support ticket.
The real-time translation feature currently supports 15 languages: Chinese, English, Spanish, Portuguese, French, German, Russian, Arabic, Japanese, Korean, Vietnamese, Malay, Indonesian, Italian, and Thai. Please contact us if you require additional languages support.
Due to variations in context and language, AI-generated translations are provided for reference only and should not be regarded as the sole professional opinion or conclusion.