Beyond Spicy Chat AI: Igniting Engagement with AI-Powered Conversational Roleplay
 The world is rapidly embracing artificial intelligence, and its impact on how we interact with technology is undeniable. One area where AI is making waves is in conversational AI, specifically with roleplay chat applications like SpicyChat AI.
The world is rapidly embracing artificial intelligence, and its impact on how we interact with technology is undeniable. One area where AI is making waves is in conversational AI, specifically with roleplay chat applications like SpicyChat AI.
SpicyChat AI is at the forefront of this exciting field, offering a unique blend of entertainment and practical utility. This platform allows users to engage in immersive roleplay scenarios with AI characters, moving beyond simple question-and-answer interactions.
SpicyChat AI: An Overview
SpicyChat AI distinguishes itself by simulating realistic conversations with virtual characters.SpicyChat AI employs various advanced algorithms to mimic real-life conversational interactions with simulated AI characters pretentiously.
Key Features:
1.Diverse AI Characters: Choose from a vast library of AI characters, each with unique personalities and backgrounds.
2.Real-time Interaction: Enjoy seamless and dynamic conversations that mimic real-life interactions.
3.Customizable Responses: Tailor AI character responses to fit specific scenarios and preferences.
4.Multi-language Support: Break down language barriers with support for multiple languages.
5.Integration Capabilities: Seamlessly integrate SpicyChat AI with various business applications and services.
The escalating demand for automating the customer support workflow, combined with the skyrocketing utilization of chatbots across a diverse range of applications - be it adult-oriented (NSFW) AI chat or AI girlfriend chat scenarios - has spurred this development.
What sets SpicyChat AI apart is its provision of top-notch, exclusive NSFW AI chat services. Tailored meticulously for adults who cherish their privacy while still yearning for engaging conversations, it strikes the perfect balance. These individuals can maintain anonymity and yet fully immerse themselves in the joy of interacting with others.
Consequently, SpicyChat AI is, in essence, revolutionizing modern communication with technology. By endowing users with a vast array of choices and powerful capabilities, it's redefining the very fabric of how we connect and converse in the digital age, making every interaction more personalized, dynamic, and fulfilling.
Why SpicyChat Holds the Key to Business Success
For business owners striving to elevate their companies to new heights amidst the surging popularity of AI chatbots, procuring an AI Clone of SpicyChat holds a wealth of significant benefits. Let's delve into the principal advantages that this clone can offer entrepreneurs:
Amplified Customer Engagement
Leveraging a multitude of AI characters and seamless real-time communication capabilities, SpicyChat AI Clone empowers customers to engage in electrifying and enjoyable conversations with brands. These interactions, brimming with excitement and novelty, not only pique the interest of consumers but also leave them thoroughly satisfied. As a result, customers are more inclined to stay loyal to the brand, enhancing customer retention rates and fostering long-term relationships that underpin business success.
Groundbreaking Marketing Strategies
Marketers today must recognize the untapped potential of NSFW chatbots in the advertising realm. These intelligent bots can be harnessed to craft highly provocative and precisely targeted advertisements. By simulating realistic scenarios that resonate deeply with the intended audience, they have the power to captivate viewers, making advertisements not just attention-grabbing but truly compelling. This novel approach allows brands to cut through the advertising clutter and forge a stronger connection with their target demographics.
Efficient Customer Support Streamlining
The remarkable performance of the AI within SpicyChat AI Clone is the driving force behind its ability to revolutionize customer support. It dispenses instant and unerring solutions to customers' queries, creating an experience that exudes warmth and friendliness. This not only delights users but also alleviates the workload on human support teams, freeing them up to focus on resolving more complex and critical issues. In doing so, it optimizes the overall efficiency of customer support operations, ensuring that every customer interaction is handled with speed and precision.
Cost-Effective Business Solution
The affordability of a SpicyChat AI Clone makes it an attractive proposition for businesses of all sizes. Commercially available and designed for easy integration, it can be seamlessly incorporated into existing business frameworks. Moreover, its flexibility allows for fine-tuning to meet the specific requirements of any particular enterprise, ensuring that it aligns perfectly with business goals and operational needs.
In a market where the demand for AI chatbot solutions is exploding, astute business people would be remiss not to seize the opportunity to acquire a SpicyChat AI Clone. Collectively, these advantages coalesce to form its unique selling points and competitive edge, equipping businesses with the tools they need to thrive and stand out in a highly competitive and saturated marketplace.
Diverse Applications of AI Chatbots
The versatility of AI chatbots like SpicyChat AI extends across various industries:
1.E-Commerce: Enhance customer service, provide product recommendations, and personalize the shopping experience.
2.Healthcare: Facilitate appointment scheduling, provide medical information, and streamline patient communication.
3.Finance and Banking: Enable balance inquiries, transaction history reviews, and offer personalized financial advice.
4.Dating Industry: Create engaging matchmaking experiences, facilitate meaningful conversations, and enhance compatibility assessments.
Build Your Own SpicyChat AI with Tencent RTC
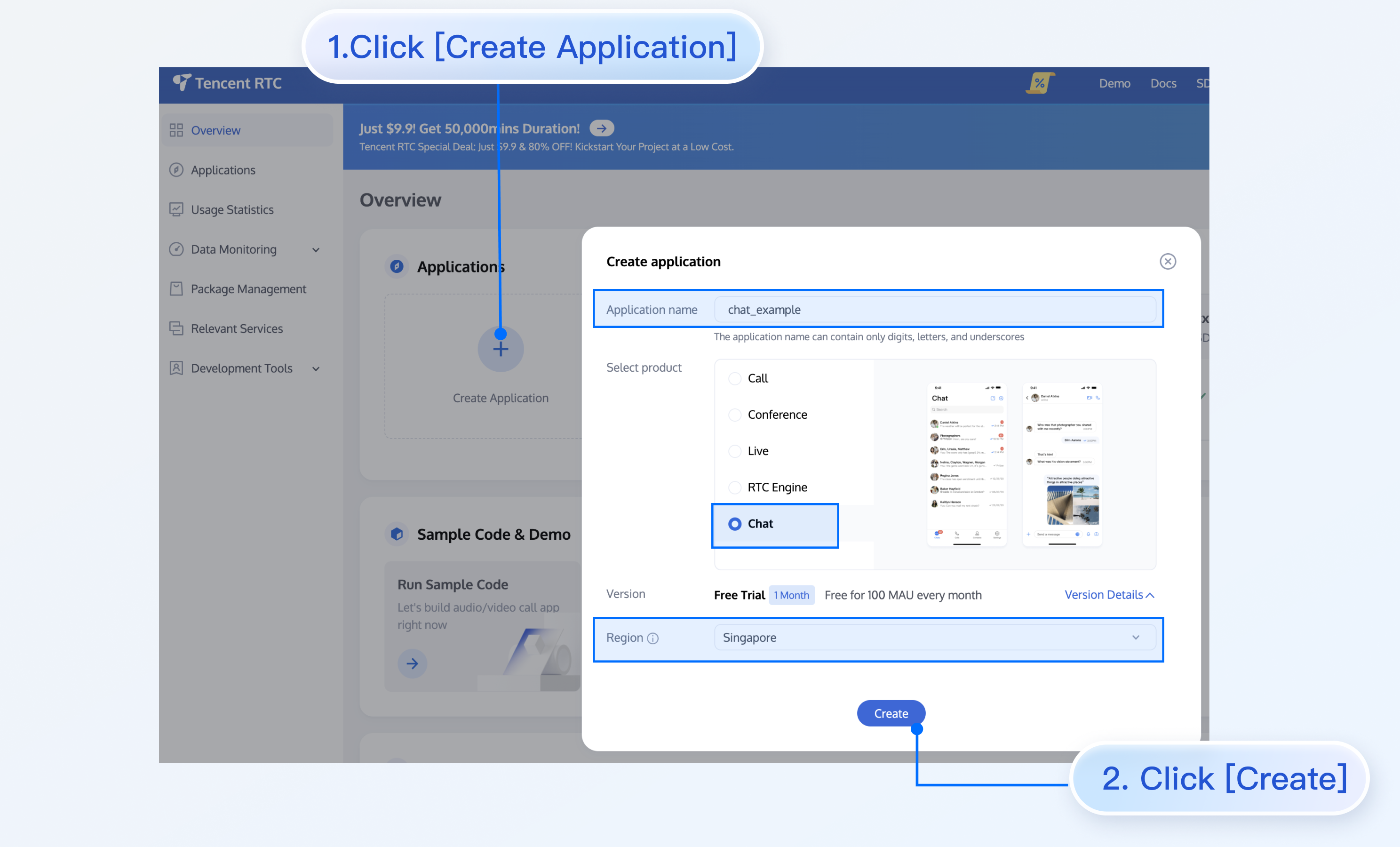
Creating a Chat account
Log in to your account, go to the console, create an application, get the application's SDKAppID and key (Chat key).
Signing up for an account with the corresponding AI service provider
Sign up for an account with the provider of the AI service to be integrated, log in, and get the API key (AI_SECRET_KEY).
Creating a Chat chatbot account
Create a Chat chatbot account through the RESTful API. The Chat chatbot is a special user whose user ID begins with @RBT#.
curl -d '{"UserID":"@RBT#001","Nick":"MyRobot"}' "https://console.tim.qq.com/v4/openim_robot_http_svc/create_robot?sdkappid= {}&identifier=administrator&usersig={}&random=123456789&contenttype=json"Replace sdkappid={} and usersig={} in the command above with your SDKAppID and the UserSig generated based on the Chat key. For more information, see Generating UserSig. After you run the command in Linux, the server returns the following information:
{"ActionStatus": "OK", "ErrorCode": 0, "ErrorInfo": ""}The information above indicates that the chatbot @RBT#001 with the nickname MyRobot was created successfully.
Configuring Chat webhooks
A Chat webhook is a request sent by the Chat backend to the backend server of the corresponding application before or after an event. The application backend can then perform the necessary data synchronization or intervene in the subsequent processing of the event. We will use a "robot event webhook" to listen for and react to user messages sent to the chatbot or @RBT# events in group chats. You need to locate and click "Robot Event Webhook" in the Chat console to enable the feature and save the settings.
Scenario-specific implementation
Taking a one-to-one chat as an example, the overall working process is as follows:
1. The user1 user sends the "hello" message to the chatbot @RBT#001.
2. The Chat backend sends a webhook to notify the application backend of the event.
3. The application backend receives the event notification which contains information such as the message sender user1, message recipient @RBT#001, and message content hello.
4. The application backend calls the AI service API (MiniMax API) and receives the response containing the reply message, such as "nice to meet you".
5. The application backend calls the Chat RESTful API (API sendmsg for a one-to-one chat and API send_group_msg for a group chat) to send the reply message to user1 as @RBT#001.
Take the Go programming language as an example, the key code of the application backend is as follows.
Note:
The following code is for demonstration only and omits a lot of exception handling code. It cannot be used directly in production environments.
Distributing and processing the webhook command
We create an HTTP service which is listened to on port 80 and register a handler with the /im URL that handles all requests sent to http://im. All webhook requests sent by Chat contain a CallbackCommand parameter, with different values representing different webhook commands. The handler performs processing according to the CallbackCommand parameter set by Chat.
func handler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
command := r.URL.Query().Get("CallbackCommand")
reqbody, _ := io.ReadAll(r.Body)
var rspbody []byte
switch command {
case "Bot.OnC2CMessage": // Chatbot’s webhook command word for a one-to-one message
dealC2c(context.Background(), reqbody)
rspbody = []byte("{\"ActionStatus\": \"OK\", \"ErrorCode\": 0, \"ErrorInfo\": \"\"}")
default:
rspbody = []byte("invalid CallbackCommand.")
}
w.Write(rspbody)
}
func main() { // Register a handler to process the webhook command sent to the application backend
http.HandleFunc("/im", handler)
http.ListenAndServe(":80", nil)
}Processing the one-to-one message received by the chatbot
When processing a one-to-one message, we first check that the sender is not a chatbot (generally a chatbot does not send a message to another chatbot) to prevent infinite webhook loops. We then parse the body of the message to obtain the content text of the message sent by the user to the chatbot, save the sender's UserID into the context to facilitate the subsequent action of calling the RESTful API to reply, and finally call askAI to request the AI service.
func dealC2c(ctx context.Context, reqbody []byte) error {
root, _ := simplejson.NewJson(reqbody)
jFromAccount := root.Get("From_Account")
fromAccount, _ = jFromAccount.String()
// Check the sender's ID to avoid processing requests sent by one chatbot to another chatbot, which leads to infinite loops.
if strings.HasPrefix(fromAccount, "@RBT#") {
return nil
}
jToAccount := root.Get("To_Account")
toAccount, _ := jToAccount.String()
msgBodyList, _ := root.Get("MsgBody").Array()
for _, m := range msgBodyList {
msgBody, _ := m.(map[string]interface{})
msgType, _ := msgBody["MsgType"].(string)
if msgType != "TIMTextElem" {
continue
}
msgContent, _ := msgBody["MsgContent"].(map[string]interface{})
text, _ := msgContent["Text"].(string)
ctx = context.WithValue(ctx, "from", fromAccount)
ctx = context.WithValue(ctx, "to", toAccount)
go askAI(ctx, text)
}
return nil
Calling the AI service API
In this step, we use a third-party AI service, MiniMax LLM, to implement intelligent chat. Any other AI service can be used instead of the MiniMax LLM service. Note that here we demonstrate a simple completion API that does not contain the context of the conversation, and you can see the MiniMax documentation for details on other APIs as needed.
type MiniMaxRsp struct {
Reply string `json:"reply"`
}
// Send a request to MiniMax and get a reply
func askAI(ctx context.Context, prompt string) {
url := "https://api.minimax.chat/v1/text/completion"
var reqData = []byte(`{
"model": "abab5-completion",
"prompt": prompt
}`)
request, _ := http.NewRequest("POST", url, bytes.NewBuffer(reqData))
request.Header.Set("Content-Type", "application/json; charset=UTF-8
request.Header.Set("Authorization", API_SECRET_KEY)
client := &http.Client{}
response, _ := client.Do(request)
defer response.Body.Close()
body, _ := ioutil.ReadAll(response.Body)
rsp := &MiniMaxRsp{}
json.Unmarshal(body, rsp)
reply(ctx, rsp.Reply) // Send the content replied by the AI service to the user
}Returning the result replied by the AI service to the user
After receiving the reply from the AI service, we only need to call the sendmsg RESTful API of Chat to simulate the chatbot to reply to the user, specifying the sender of the message as @RBT#001 and the recipient as user1.
// Send a RESTful API request
func doRestAPI(host string, sdkappid int, admin, usersig, command, body string) {
url := fmt.Sprintf("https://%s/v4/%s?sdkappid=%d&identifier=%s&usersig=%s&random=%d&contenttype=json",
host, command, sdkappid, admin, usersig, rand.Uint32())
req, _ := http.NewRequest("POST", url, bytes.NewBufferString(body))
req.Header.Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
cli := &http.Client{}
rsp, err := cli.Do(req)
if err != nil {
log.Printf("REST API failed. %s", err.Error())
return
}
defer rsp.Body.Close()
rsptext, _ := io.ReadAll(rsp.Body)
log.Printf("rsp:%s", rsptext)
}
// Call the RESTful API of Chat to reply to the user
func reply(ctx context.Context, text string) {
rsp := make(map[string]interface{})
msgbody := []map[string]interface{}{{
"MsgType": "TIMTextElem",
"MsgContent": map[string]interface{}{"Text": text},
}}
// For the implementation of `GenUserSig`, see the documentation.
usersig, _ := GenUserSig(IM_SDKAPPID, IM_KEY, "administrator", 60)
rsp["From_Account"] = ctx.Value("to").(string) //"@RBT#001"
rsp["To_Account"] = ctx.Value("from").(string)
rsp["SyncOtherMachine"] = 2
rsp["MsgLifeTime"] = 60 * 60 * 24 * 7
rsp["MsgSeq"] = rand.Uint32()
rsp["MsgRandom"] = rand.Uint32()
rsp["MsgBody"] = msgbody
rspbody, _ := json.Marshal(rsp)
doRestAPI("console.tim.qq.com", IM_SDKAPPID, "administrator", usersig, "openim/sendmsg", string(rspbody))
}Effect Demonstration
The following demonstrates the final implementation effect of the Chat chatbot demo:
With the above steps, we have implemented one-to-one chat connectivity between the Chat server side and the MiniMaxAI open platform. It is also possible to integrate AI services from another AI service provider following the above steps by simply replacing the askAI function with the corresponding API call from that AI service provider. For group chat chatbots, only the implementation of the Bot.OnGroupMessage webhook command processing needs to be supplemented.
Order Now
Click here to quickly go to the purchase page to order.


